Page 19 - Azerbaijan State University of Economics
P. 19
THE JOURNAL OF ECONOMIC SCIENCES: THEORY AND PRACTICE, V.70, # 2, 2013, pp. 4-31
modernism period developed in 70-80s of XX century. Although some portion of modern
approached is widely accepted, points related to the time understanding were conceptually
changed. The time already accepted the completeness feature. In postmodernism the time is
revocable and repeating – unlike in traditional society – we talk about “postmodernism repeat”.
The existence of time flows like past present future and wise versa are treated from
discrete point of view.
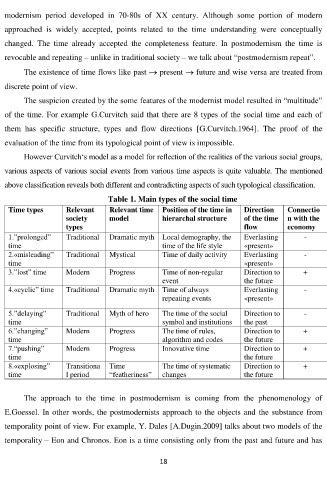
The suspicion created by the some features of the modernist model resulted in “multitude”
of the time. For example G.Curvitch said that there are 8 types of the social time and each of
them has specific structure, types and flow directions [G.Curvitch.1964]. The proof of the
evaluation of the time from its typological point of view is impossible.
However Curvitch‘s model as a model for reflection of the realities of the various social groups,
various aspects of various social events from various time aspects is quite valuable. The mentioned
above classification reveals both different and contradicting aspects of such typological classification.
Table 1. Main types of the social time
Time types Relevant Relevant time Position of the time in Direction Connectio
society model hierarchal structure of the time n with the
types flow economy
1.”prolonged” Traditional Dramatic myth Local demography, the Everlasting -
time time of the life style «present»
2.«misleading” Traditional Mystical Time of daily activity Everlasting -
time «present»
3.”lost” time Modern Progress Time of non-regular Direction to +
event the future
4.«cyclic” time Traditional Dramatic myth Time of always Everlasting -
repeating events «present»
5.”delaying” Traditional Myth of hero The time of the social Direction to -
time symbol and institutions the past
6.”changing” Modern Progress The time of rules, Direction to +
time algorithm and codes the future
7.“pushing” Modern Progress Innovative time Direction to +
time the future
8.«explosing” Transitiona Time The time of systematic Direction to +
time l period “featheriness” changes the future
The approach to the time in postmodernism is coming from the phenomenology of
E.Goessel. In other words, the postmodernists approach to the objects and the substance from
temporality point of view. For example, Y. Dales [A.Dugin.2009] talks about two models of the
temporality – Eon and Chronos. Eon is a time consisting only from the past and future and has
18