Page 135 - Azerbaijan State University of Economics
P. 135
THE JOURNAL OF ECONOMIC SCIENCES: THEORY AND PRACTICE, V.71, # 1, 2014, pp. 127-139
Overall 35 references and publication outcomes were integrated in the simulation model
and connected according to the illustrated methodology in figure 2. For the results of this
simulation the original source data of the german simulation - where original data was missing –
was interpolated: over source data context like cost of hospital days or where nothing else was
available over the per capita spending Germany vs. AR [Implementing Health Sector Reform in
Central Asia: Papers from a Health Policy Seminar Held in Ashgabat, Turkmenistan in June,
1996 Zuzana Feachem, Martin Hensher, Laura Rose, World Bank Publications, 1999]. The main
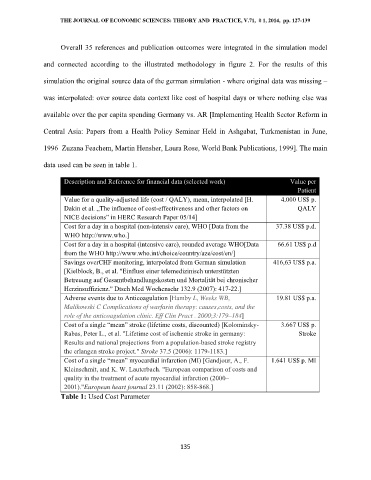
data used can be seen in table 1.
Description and Reference for financial data (selected work) Value per
Patient
Value for a quality-adjusted life (cost / QALY), mean, interpolated [H. 4.000 US$ p.
Dakin et al. „The influence of cost-effectiveness and other factors on QALY
NICE decisions” in HERC Research Paper 05/14]
Cost for a day in a hospital (non-intensiv care), WHO [Data from the 37.38 US$ p.d.
WHO http://www.who.]
Cost for a day in a hospital (intensive care), rounded average WHO[Data 66.61 US$ p.d
from the WHO http://www.who.int/choice/country/aze/cost/en/]
Savings overCHF monitoring, interpolated from German simulation 416,63 US$ p.a.
[Kielblock, B., et al. "Einfluss einer telemedizinisch unterstützten
Betreuung auf Gesamtbehandlungskosten und Mortalität bei chronischer
Herzinsuffizienz." Dtsch Med Wochenschr 132.9 (2007): 417-22.]
Adverse events due to Anticoagulation [Hamby L, Weeks WB, 19.81 US$ p.a.
Malikowski C Complications of warfarin therapy: causes,costs, and the
role of the anticoagulation clinic. Eff Clin Pract . 2000;3:179–184]
Cost of a single “mean” stroke (lifetime costs, discounted) [Kolominsky- 3.667 US$ p.
Rabas, Peter L., et al. "Lifetime cost of ischemic stroke in germany: Stroke
Results and national projections from a population-based stroke registry
the erlangen stroke project." Stroke 37.5 (2006): 1179-1183.]
Cost of a single “mean” myocardial infarction (MI) [Gandjour, A., F. 1.641 US$ p. MI
Kleinschmit, and K. W. Lauterbach. "European comparison of costs and
quality in the treatment of acute myocardial infarction (2000–
2001)."European heart journal 23.11 (2002): 858-868.]
Table 1: Used Cost Parameter
135