Page 59 - Azerbaijan State University of Economics
P. 59
THE JOURNAL OF ECONOMIC SCIENCES: THEORY AND PRACTICE, V.70, # 2, 2013, pp. 32-66
mentioned above, would be the instruments that can be changed, to reflect policy choices and
directions, and hence, the changed values would affect the next run of the model, and creating
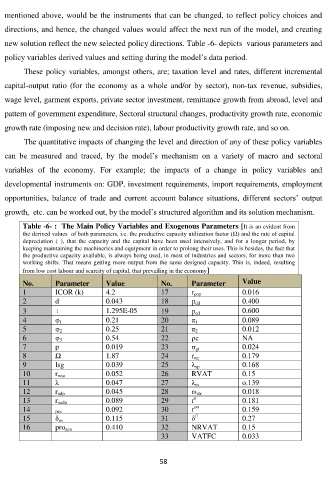
new solution reflect the new selected policy directions. Table -6- depicts various parameters and
policy variables derived values and setting during the model’s data period.
These policy variables, amongst others, are; taxation level and rates, different incremental
capital-output ratio (for the economy as a whole and/or by sector), non-tax revenue, subsidies,
wage level, garment exports, private sector investment, remittance growth from abroad, level and
pattern of government expenditure, Sectoral structural changes, productivity growth rate, economic
growth rate (imposing new and decision rate), labour productivity growth rate, and so on.
The quantitative impacts of changing the level and direction of any of these policy variables
can be measured and traced, by the model’s mechanism on a variety of macro and sectoral
variables of the economy. For example; the impacts of a change in policy variables and
developmental instruments on: GDP, investment requirements, import requirements, employment
opportunities, balance of trade and current account balance situations, different sectors’ output
growth, etc. can be worked out, by the model’s structured algorithm and its solution mechanism.
Table -6- : The Main Policy Variables and Exogenous Parameters [It is an evident from
the derived values of both parameters, i.e. the productive capacity utilization factor (Ω) and the rate of capital
depreciation (ԃ), that the capacity and the capital have been used intensively, and for a longer period, by
keeping maintaining the machineries and equipment in order to prolong their uses. This is besides, the fact that
the productive capacity available, is always being used, in most of industries and sectors, for more than two
working shifts. That means getting more output from the same designed capacity. This is, indeed, resulting
from low cost labour and scarcity of capital, that prevailing in the economy]
No. Parameter Value No. Parameter Value
1 ICOR (k) 4.2 17 r pop 0.016
2 d 0.043 18 p dd 0.400
3 ɩ 1.295E-05 19 p ed 0.600
4 φ 1 0.21 20 π 1 0.089
5 φ 2 0.25 21 π 2 0.012
6 φ 3 0.54 22 ρc NA
7 p 0.019 23 σ gt 0.024
8 Ω 1.87 24 r eg 0.179
9 lѕg 0.039 25 λ sp 0.168
10 r wsa 0.052 26 RVAT 0.15
11 λ 0.047 27 λ es o.139
12 r adp 0.045 28 ω ntr 0.018
e
13 r nadp 0.089 29 r 0.181
on
14 pes 0.092 30 r 0.159
fi
15 δ os 0.115 31 δ 0.27
16 pro gco 0.410 32 NRVAT 0.15
33 VATFC 0.033
58