Page 21 - Azerbaijan State University of Economics
P. 21
THE JOURNAL OF ECONOMIC SCIENCES: THEORY AND PRACTICE, V.78, # 2, 2021, pp. 17-42
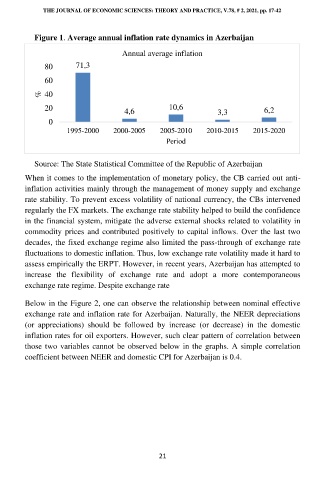
Figure 1. Average annual inflation rate dynamics in Azerbaijan
Annual average inflation
80 71,3
60
% 40
20 4,6 10,6 3,3 6,2
0
1995-2000 2000-2005 2005-2010 2010-2015 2015-2020
Period
Source: The State Statistical Committee of the Republic of Azerbaijan
When it comes to the implementation of monetary policy, the CB carried out anti-
inflation activities mainly through the management of money supply and exchange
rate stability. To prevent excess volatility of national currency, the CBs intervened
regularly the FX markets. The exchange rate stability helped to build the confidence
in the financial system, mitigate the adverse external shocks related to volatility in
commodity prices and contributed positively to capital inflows. Over the last two
decades, the fixed exchange regime also limited the pass-through of exchange rate
fluctuations to domestic inflation. Thus, low exchange rate volatility made it hard to
assess empirically the ERPT. However, in recent years, Azerbaijan has attempted to
increase the flexibility of exchange rate and adopt a more contemporaneous
exchange rate regime. Despite exchange rate
Below in the Figure 2, one can observe the relationship between nominal effective
exchange rate and inflation rate for Azerbaijan. Naturally, the NEER depreciations
(or appreciations) should be followed by increase (or decrease) in the domestic
inflation rates for oil exporters. However, such clear pattern of correlation between
those two variables cannot be observed below in the graphs. A simple correlation
coefficient between NEER and domestic CPI for Azerbaijan is 0.4.
21