Page 49 - Azerbaijan State University of Economics
P. 49
Fatih Chellai: Regime-Dependent Effects of Public Spending in Algeria: A Structural VAR and
Markov-Switching Approach
Furthermore, the cumulative test for lags 1 to 2 confirms this conclusion with a p-
value of 0.4552. These results suggest that the VAR model's residuals are well
behaved and that the model's dynamics are correctly specified, reinforcing the
reliability of the resulting estimates and analyses.
Normality test
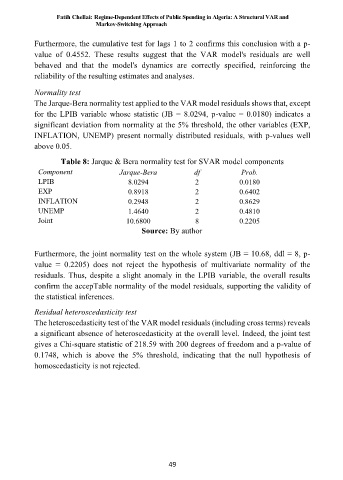
The Jarque-Bera normality test applied to the VAR model residuals shows that, except
for the LPIB variable whose statistic (JB = 8.0294, p-value = 0.0180) indicates a
significant deviation from normality at the 5% threshold, the other variables (EXP,
INFLATION, UNEMP) present normally distributed residuals, with p-values well
above 0.05.
Table 8: Jarque & Bera normality test for SVAR model components
Component Jarque-Bera df Prob.
LPIB 8.0294 2 0.0180
EXP 0.8918 2 0.6402
INFLATION 0.2948 2 0.8629
UNEMP 1.4640 2 0.4810
Joint 10.6800 8 0.2205
Source: By author
Furthermore, the joint normality test on the whole system (JB = 10.68, ddl = 8, p-
value = 0.2205) does not reject the hypothesis of multivariate normality of the
residuals. Thus, despite a slight anomaly in the LPIB variable, the overall results
confirm the accepTable normality of the model residuals, supporting the validity of
the statistical inferences.
Residual heteroscedasticity test
The heteroscedasticity test of the VAR model residuals (including cross terms) reveals
a significant absence of heteroscedasticity at the overall level. Indeed, the joint test
gives a Chi-square statistic of 218.59 with 200 degrees of freedom and a p-value of
0.1748, which is above the 5% threshold, indicating that the null hypothesis of
homoscedasticity is not rejected.
49